Heart Attack and Stroke Warning Signs
Heart attack and stroke are life threatening emergencies. If you see someone who has any of the listed symptoms, immediately call 9-1-1. Not all of these signs occur in every heart attack or stroke victim, sometimes they go away and return. If some occur, get help fast!
Today, heart attack and stroke victims can benefit from new medications and treatments unavailable in the past. Clot-busting drugs can stop some heart attacks and strokes in progress, reducing disability and saving lives. To be effective, these drugs must be given relatively quickly after heart attack or stroke symptoms first appear.
Coronary heart disease is America’s No. 1 killer. Stroke is No. 3 and a leading cause of serious disability, know the warning signs, and know how to respond quickly and properly if warning signs occur. One million people die from heart disease and 700,000 people have a stroke annually.
The Same Things That Cause Accidents Cause Near Misses:
A heart attack is a result of two processes. One is the gradual and slow narrowing of the coronary arteries which supply the heart muscle with blood (hardening of the arteries); the second is a sudden and abrupt blockage of the artery due to the development of a blood clot (coronary thrombosis) in the narrow artery.
The result is a sudden cut off in the nutrients and oxygen supply to the heart muscle. The tissue, hence, gets damaged and the heart muscle is replaced by scar tissue.
Luckily, the heart has considerable reserve capacity, as a pump, and so a small amount of damage may not interfere with the ability of the heart to pump reasonable amounts of blood around the body. Thus, a patient can often recover well and return to a fairly normal life.

Heart Attack Warning Signs
Some heart attacks are sudden and intense but most heart attacks start slowly, with mild pain or discomfort. Often people affected aren’t sure what’s wrong and wait too long before getting help. Here are signs that can mean a heart attack is happening:
- Pain, fullness, and/or squeezing sensation of the chest
- Jaw pain, toothache, headache
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea, vomiting, and/or general epigastric discomfort (upper middle abdomen)
- Sweating
- Heartburn and/or indigestion
- Arm pain (more commonly the left arm, but may be either arm)
- Upper back pain
- General malaise (vague feeling of illness)
If you or someone you’re with has chest discomfort, especially with one or more of the other signs, don’t wait longer than a few minutes (no more than 5) before calling for help. Calling 9-1-1 is almost always the fastest way to get lifesaving treatment.
If you can’t access the emergency medical services (EMS), have someone drive you to the hospital right away. If you’re the one having symptoms, don’t drive yourself, unless you have absolutely no other option.
As with men, women’s most common heart attack symptom is chest pain or discomfort. But women are somewhat more likely than men to experience some of the other common symptoms, particularly shortness of breath, nausea/vomiting, and back or jaw pain.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest strikes immediately and without warning.
Here are the signs:
- Sudden loss of responsiveness.
- No response to gentle shaking.
- No normal breathing. The victim does not take a normal breath when you check for several seconds.
- No signs of circulation.
- No movement or coughing.
- If cardiac arrest occurs, call 9-1-1 and begin CPR immediately. If an automated external defibrillator (AED) is available and someone is trained to use it, involve them.
What is a Stroke?
The most common cause of a stroke is when a blood vessel supplying these vital nutrients to the brain becomes blocked with a blood clot.
The blood clot – known as a thrombosis – may form locally in a brain artery or form elsewhere (for example, in the heart) and travel in the bloodstream to lodge in the brain. This type of wandering clot is known as an embolus.
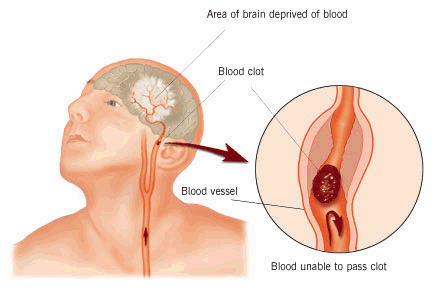
When a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked, the brain cells that it supplies quickly become starved of oxygen and glucose, and stop working properly. If the blood supply is not quickly resumed, these brain cells will die.
This type of stroke is called an ischemic stroke, or a ‘cerebral infarct’. The medical term ‘ischemic ’ means a shortage of blood. ‘Cerebral’ is the medical term for the brain and ‘infarct’ is the medical term for death of a part of the body
The second most common cause of a stroke is a brain hemorrhage, which occurs when a blood vessel bursts inside the head. As well as disrupting the supply of oxygen and glucose to some parts of the brain, the escaping blood can cause damage by clotting, swelling and triggering inflammation.
Stroke Warning Signs
The American Stroke Association says these are the warning signs of stroke:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden, severe headache with no known cause
Sometimes symptoms of a stroke are difficult to identify. Unfortunately, the lack of awareness spells disaster. The stroke victim may suffer severe brain damage when people nearby fail to recognize the symptoms of a stroke. If you suspect someone is having a stroke, doctors say a bystander can recognize a stroke by asking three simple questions:
- Ask the individual to “smile”.
- Ask the person to “talk”. Speak a simple sentence (coherently i.e. . . It is sunny out today)
- Ask him or her to “raise both arms”.
- Given the list of symptoms, it is easy to see how these three simple questions could help identify a stroke.
However, there is an important point that needs to be considered. While the central information is true, the absence of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate that a person is not having a stroke.
It could be extremely dangerous to reach the conclusion that a person did not require medical attention just because he or she could successfully carried out the three steps outlined in the test.
If you or someone with you has one or more of these signs, immediately call 9-1-1. Also, check the time so you’ll know when the first symptoms appeared. It’s very important to take immediate action.
If given within three hours of the start of symptoms, a clot-busting drug can reduce long-term disability for the most common type of stroke.